As we have benefited from animals from the past to the present, protecting their health, protecting and monitoring them is one of our basic duties for sustainability. In order to take sick animals to a safe area and start the treatment process or to identify lost animals, they must be given an identity card.
Identification of Animals
As we have benefited from animals from the past to the present, protecting their health, protecting and monitoring them is one of our basic duties for sustainability. In order to take sick animals to a safe area and start the treatment process or to identify lost animals, they must be given an identity card. Thanks to this identity, we can register animals, count them and keep them under our control. In this article, we will discuss passive RFID tags that will replace the old animal tags. If you want to see the types of animal tags with RFID technology and get information about how to obtain them, you can visit our related page.

Electronic Tagging of Animals
The purpose of tagging and registering animals is to record these assets, which are intended to be tracked, with a unique identity. RFID tracking systems, which provide many benefits such as controlling animal movements, tracking vaccination periods, ownership information, preventing the spread of diseases by preventing the movement of diseased animals and thus protecting public health by obtaining healthy food, also make a significant contribution to the formation of big data that will have an impact on decision-making processes in the future. It has been made compulsory to keep the animal passport with the animals in the intra-provincial transfers of bovine animals and the transport document with the animals in the intra-provincial transfers of ovine animals, and in the coming periods, the use of RFID technology in identification will be spread much more rapidly by the authorities as a security-enhancing factor. In the inter-provincial transfers of bovine and ovine animals, the Veterinary Health Report issued on the basis of these documents is required after the inspection control of the animals.
How RFID is Transforming the Livestock Management Industry
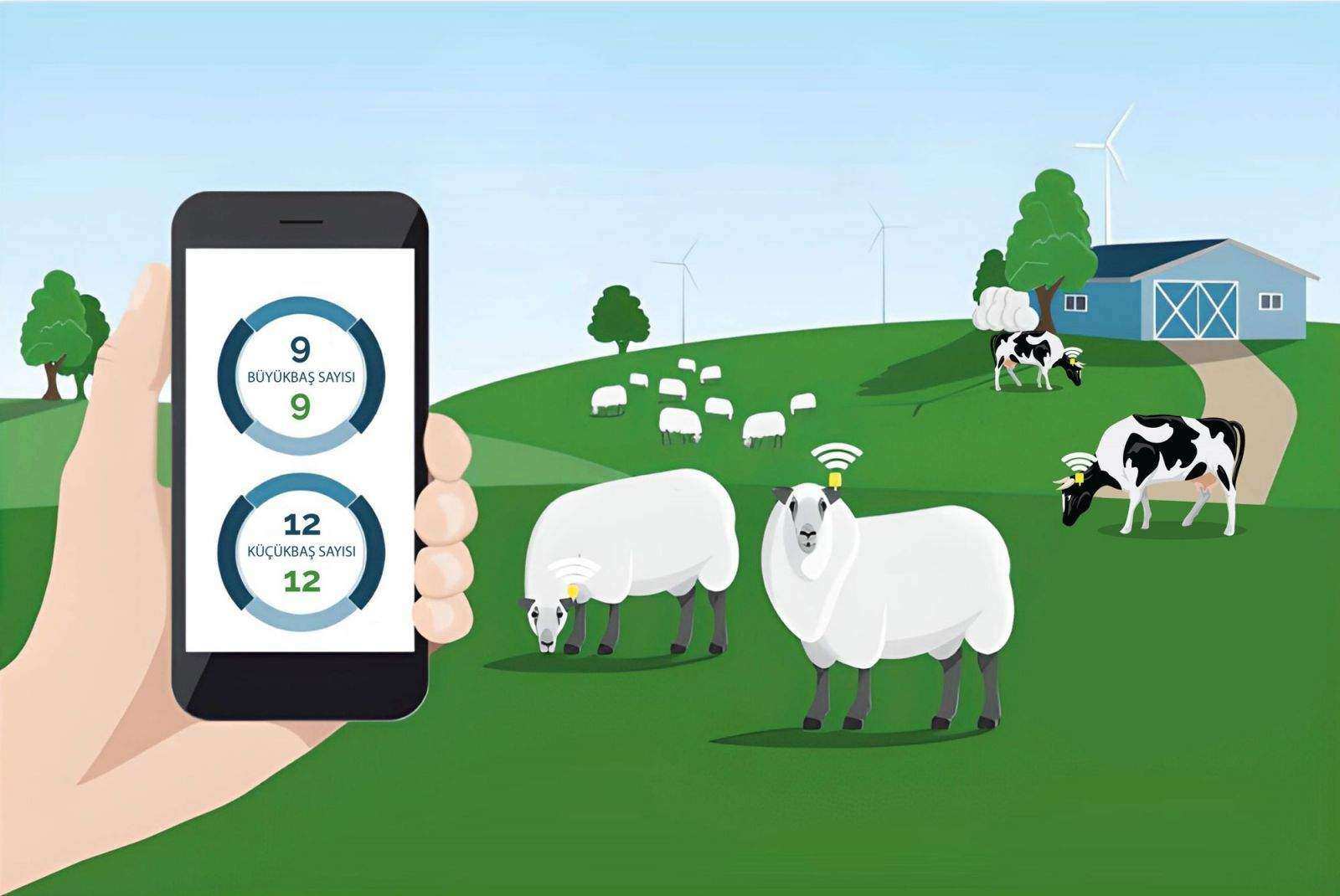
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology is spreading to a large number of industries, including animal husbandry. RFID technology was started to be used in the mid-1900s, and with the decrease in application and infrastructure costs, it was started to be used under the name of animal identification in 2000. Thanks to the use of RFID, animals can be counted quickly and accurately.
How Do Passive RFID Tags Work in Livestock Management?
In livestock management, RFID is used to identify and track individual animals, including ovine (sheep, goats, etc.) and bovine (cows, cattle, etc.). A tamper-proof RFID tag in a durable plastic case is attached to each animal's ear with easy-to-use ear tag attachment pliers. Many tags consist of two discs that are joined together through the animal's ear. The process is similar to piercing a human ear. Each tagged animal is given a different tracking number and counting is initiated with RFID readers. The data collected from the readers are transferred to the facility's computer system, which can be connected to cloud-based tracking systems over the internet. Thus, counts are made quickly.
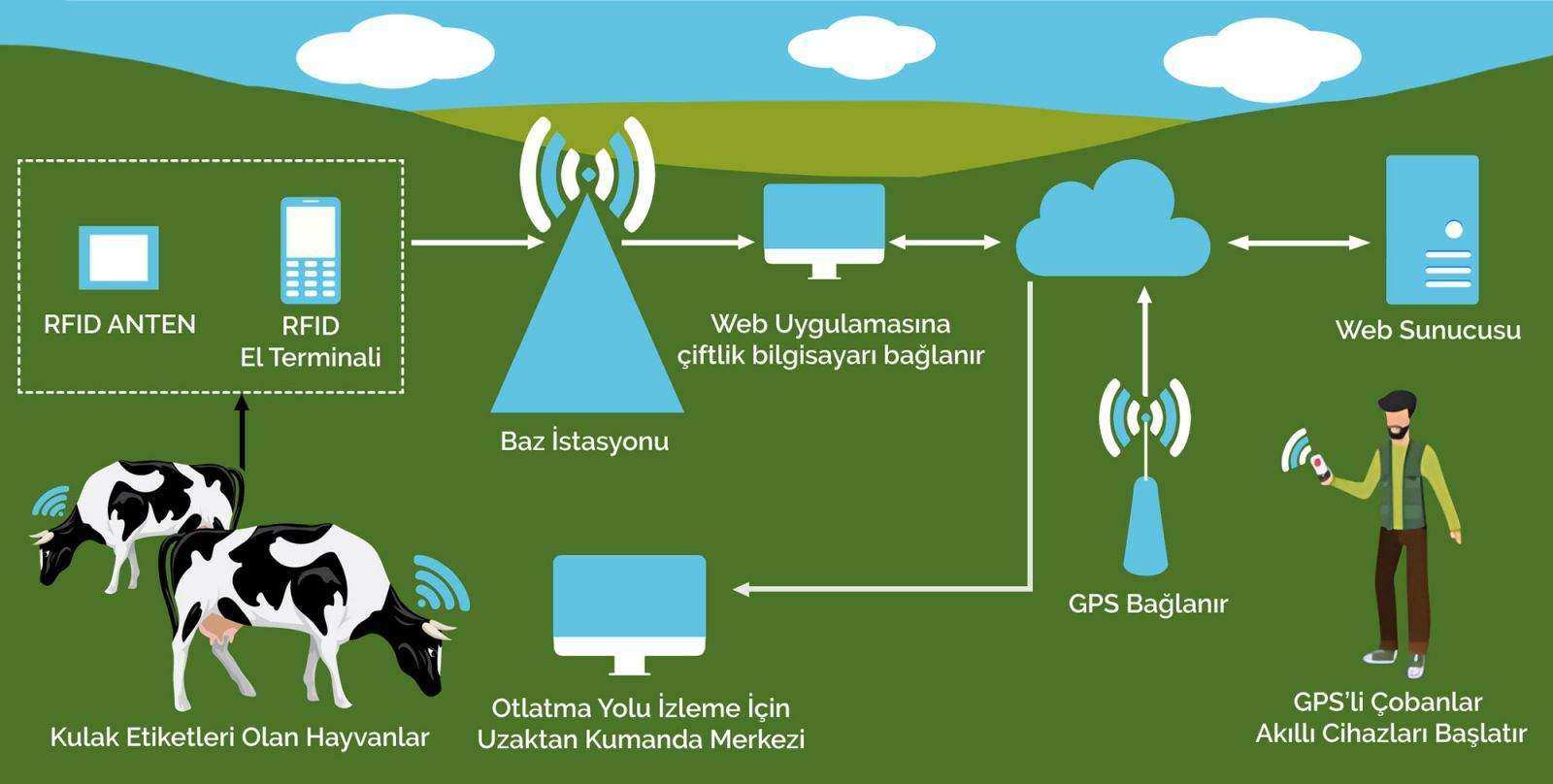
How to Use RFID in Livestock Management?
Farmers need to quickly and easily identify their animals during inventory recording. Traditionally, farmers have used metal identification tags attached to the animals' ears for this purpose. RFID tags are replacing metal tags as they offer significantly improved functionality. The old metal tags had to be visually read by farmers, which was time-consuming and resulted in numerous errors. In addition, due to their size, old-style tags can get caught in surrounding machinery or objects, causing them to become loose and subsequently lost.
RFID tags, on the other hand, are more durable than traditional metal tags. They are read electronically rather than visually, which eliminates human error in the process. The tags do not require the animals to be completely still for them to be read, so they can be counted while feeding, in the field, in the canal or anywhere else they are.
Benefits of RFID Technology in Livestock Industry and Smart Farming
- RFID tags allow farmers to do more than just identify individual animals. The tags and accompanying software can store an animal's complete history, including its weight, age, sex, time of birth, offspring and medical records. For example, veterinarians only need to scan an animal's Rfid tag to obtain detailed information about its health. It's all part of the trend towards 'smart farming', utilising Internet of Things (IoT) technologies, which is taking the livestock sector completely under control. With accurate data collected, farmers can better manage milking, feeding, breeding and other activities from birth to slaughter. Farmers who adopt RFID technology gain a competitive advantage over those who continue to use traditional tracking methods. RFID provides many important advantages, including the following:
- Time and labour saving,
- Faster identification and control of diseased animals,
- Safer tracking of animals,
- Authentication of animals,
- Identification and monitoring of livestock inventories.
 *https://rfidjournallive.com/content/blog/how-rfid-is-transforming-the-livestock-management-industry/
*https://rfidjournallive.com/content/blog/how-rfid-is-transforming-the-livestock-management-industry/
** About Individual Identification of Animals from Birth to Sale in the World;
In many countries in the world, there are compulsory or voluntary systems for the traceability of meat and meat products. Regarding the traceability systems for cattle and beef, the EU and Japan have fully implemented the programme of tracing animals from birth to sale with their individual IDs through legal regulations. The implementation of the same compulsory system in South Korea and China is in the planning stage. Namibia and Botswana, which export beef to EU countries, have a compulsory traceability system from birth to slaughter. In some countries, although there is no mandatory legal regulation, the same system is applied voluntarily (Smith et al. 2008). The EU has made traceability of sheep and mutton and pork and pork meat from birth to sale with individual identification and traceability programmes compulsory with legal regulations (EC 2002, EC 2004, EC 2006).
In our country, the concept of traceability has been tried to be defined with the Law No. 5179 "On the Amendment and Adoption of the Decree Law on the Production, Consumption and Supervision of Foods" (KKGM, 2004), which was published in the Official Gazette No. 25483 on 5 June 2004 within the framework of the European Union acquis. However, there is still no system in place to control the traceability of animals in the food chain and their slaughterhouse records and meat.
** The Use of RFID Technology in the Traceability and Tracking of Meat and Meat Products from Farm to Table (Istanbul University Institute of Health Sciences /Pelin Burcu Daştan, Master's thesis)